Products
At Shribhairav Forge, we specialize in providing a comprehensive range of high-quality industrial piping components designed to meet the demanding needs of diverse industries. Our product portfolio includes precision-engineered flanges, pipe fittings, forged fittings, and fasteners, all manufactured from superior-grade materials for durability, corrosion resistance, and optimal performance. Each component is meticulously crafted to international standards, ensuring reliable connections and long service life in critical applications such as oil & gas, petrochemical, power generation, and marine industries.
In addition, we supply premium compression tube fittings, pipes, tubes, rods, bars, and valves that offer exceptional strength, leak-proof integrity, and dimensional accuracy. Available in various materials, sizes, and specifications, our products are designed to handle high-pressure and high-temperature environments with ease. Whether you need custom-engineered solutions or standard components, Shribhairav Forge delivers quality, precision, and consistency — making us a trusted partner for all your piping and flow control requirements.
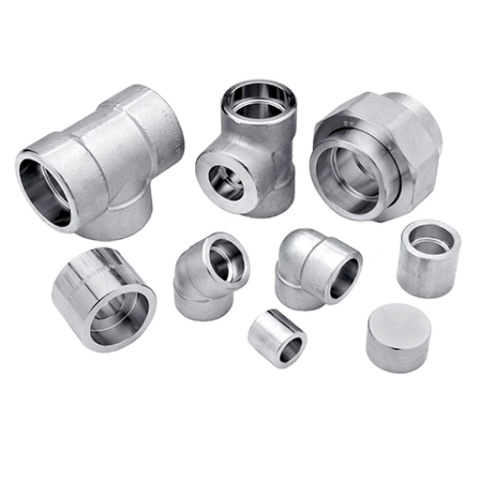
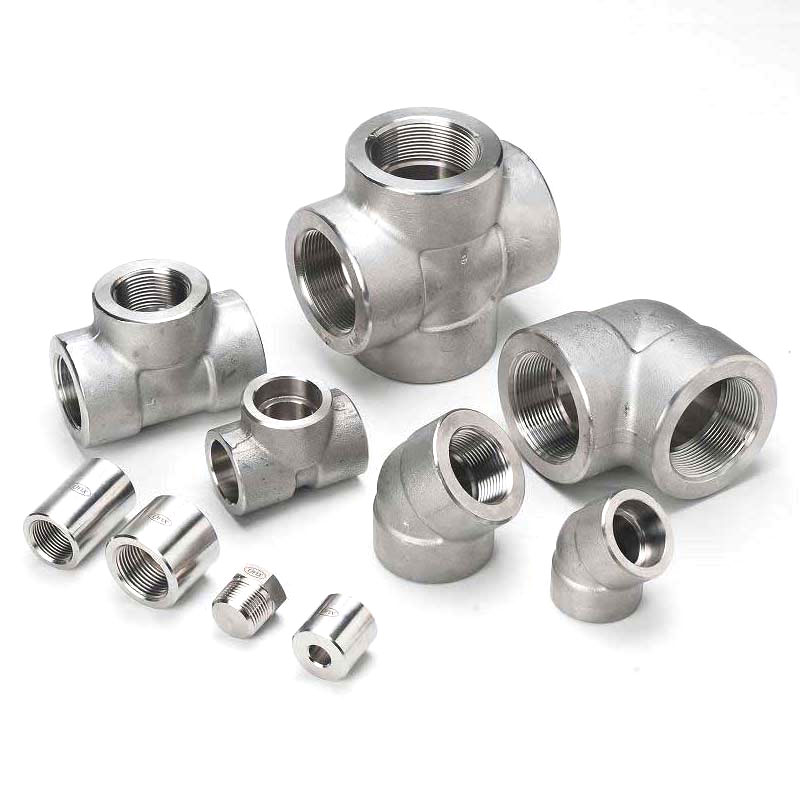
Forged socket weld fittings manufacturer and exporter in India
Forged threaded pipe fittings for high-pressure applications
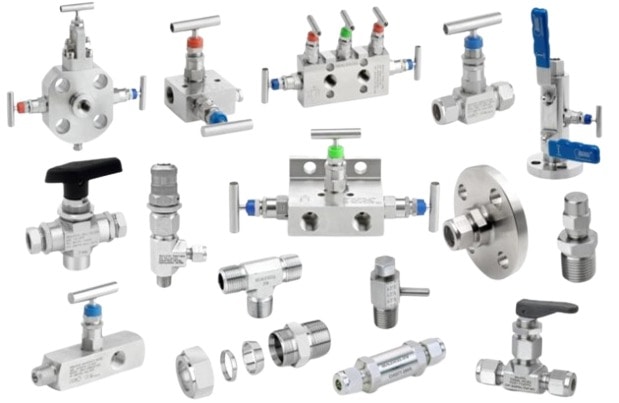
Precision-engineered Compression Tube Fittings Manufacturer for instrumentation
Manufacturer & Exporter of Instrumentation valves for oil, gas, and refinery projects
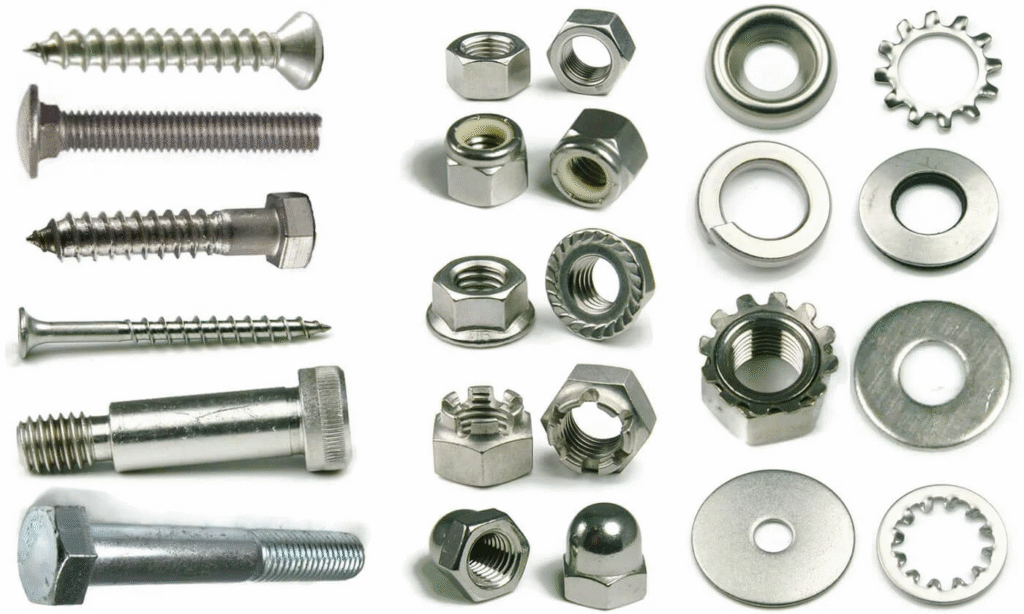
High-tensile Fasteners – bolts, nuts, and screws for heavy industries. Complete Range of Fasteners Products under one roof.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using forged steel fittings Products over cast fittings Products?
While both forged and cast fittings Products serve to connect pipes, the manufacturing process gives forged steel fittings a distinct set of advantages in terms of performance and reliability.
The primary benefit of forging is that it creates a refined grain structure that is denser and more uniform than in casting. This results in superior mechanical properties:
Greater Strength and Durability: The forging process eliminates internal defects like porosity and shrinkage, resulting in a fitting that can withstand higher pressures, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress without failing.
Improved Structural Integrity: The continuous grain flow of a forged fitting follows the shape of the part, providing higher impact resistance and fatigue strength. This means a longer service life, especially in vibrating or high-stress environments.
Enhanced Leak Resistance: Due to their dense, non-porous structure, forged fittings provide a more reliable and leak-proof seal, which is critical for transporting hazardous materials or in high-pressure gas lines.
Consistent Quality: Forging is a highly controlled process that produces fittings with consistent metallurgical properties and dimensional accuracy from piece to piece.
How do I select the correct type of flange for my application?
Selecting the correct flange is essential for creating a secure and serviceable connection between pipes, valves, and pumps. The choice depends on several key factors related to your specific application.
Here’s a look at common flange types and their uses:
Weld Neck Flange: Features a long, tapered hub that is welded to the pipe. It provides excellent stress distribution and is the preferred choice for high-pressure, high-temperature, and hazardous fluid applications.
Slip-On Flange: Slides over the pipe and is then welded in place (both inside and outside). It is easier to install than a weld neck but has lower strength, making it suitable for lower-pressure applications.
Blind Flange: A solid disc used to seal the end of a pipe or to terminate a piping system. It allows for easy access for future system expansion.
Threaded Flange: Screws onto a threaded pipe. It is used in applications where welding is not possible or practical, such as in explosive areas. Best for low-pressure systems.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Flange:
Pressure-Temperature Rating: Ensure the flange’s class (e.g., 150#, 300#) can handle the operating pressure and temperature of your system.
Pipe Material: The flange material should be compatible with the pipe material to prevent corrosion.
Connection Type: Determine if you need to weld, screw, or bolt the connection.
Media: Consider the fluid or gas being transported to ensure material compatibility and corrosion resistance.
What are instrumentation valves, and what are their common applications?
Instrumentation valves are specialized valves designed for high precision, control, and measurement within a process system. Unlike standard valves that simply turn flow on or off, instrumentation valves allow for fine-tuning of flow rates, isolating instruments for maintenance, and ensuring system accuracy.
Key types and their functions include:
Needle Valves: Allow for very precise regulation of flow rate. They are ideal for controlling the flow to sensitive gauges and meters.
Ball Valves: Offer quick, quarter-turn shut-off. In instrumentation, they are often used to isolate instruments or system sections.
Check Valves: Permit flow in only one direction, preventing backflow that could damage instruments or contaminate a process.
Manifold Valves: A complex valve body that combines multiple valves into one unit. They are used to isolate and equalize pressure for differential pressure transmitters.
Common Applications:
Instrumentation valves are essential in any industry requiring precise process control, including:
Oil and Gas refining
Petrochemical and chemical processing plants
Power generation facilities
Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Laboratories and research facilities
They are also used in applications like instrument isolation, gauge calibration, sampling lines, and flow regulation.
What are the main differences between buttweld, socket weld, and threaded pipe fittings?
Choosing the right product in pipe fitting is crucial for the safety and longevity of any piping system. The primary differences between buttweld, socket weld, and threaded fittings products lie in their connection method, strength, and typical applications.
Buttweld (BW) Fittings:
Connection: These fittings are beveled at each end and are welded directly, edge-to-edge, onto the pipe. This creates a continuous, strong, and leak-proof connection that becomes part of the pipe itself.
Strength: Buttweld fittings offer the highest strength and structural integrity, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Applications: Commonly used in industrial pipelines for oil, gas, chemicals, and power plants where performance under stress is critical.
Tip: Link to your Buttweld Pipe Fittings category page here.
Socket Weld (SW) Fittings:
Connection: The pipe is inserted into a recessed area (a “socket”) of the fitting. It is then secured with a fillet weld around the top of the fitting.
Strength: Provides a strong connection, though generally rated for lower pressures than buttweld fittings. Installation can be easier as it doesn’t require beveled ends.
Applications: Used in areas where frequent leakage is a concern, such as in chemical processing and hydraulic systems for smaller pipe diameters (typically under 2 inches).
Tip: Link to your Forged Socket Weld Pipe Fittings category page here.
Forged Threaded Fittings:
Connection: These fittings have threads (male or female) that screw directly onto the threaded pipe. Sealants are often used to ensure a leak-free joint.
Strength: The easiest to install and disassemble, but they are the weakest of the three types, making them suitable for low-pressure and low-temperature systems.
Applications: Ideal for non-critical applications like plumbing, fire protection, and industrial cooling water systems where welding is not feasible or necessary.
What should I consider when choosing industrial fasteners for a project?
Industrial fasteners, including bolts, nuts, screws, and washers, are critical components that hold everything together. Choosing the right one is vital for safety and structural integrity.
Here are the key factors to consider:
Material: The material dictates the fastener’s strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for different environments.
Carbon Steel: Offers high strength but requires a protective coating (like zinc) to resist rust.
Stainless Steel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor, marine, or chemical environments.
Alloy Steel: Enhanced with elements like chromium or molybdenum for extreme strength and temperature resistance.
Strength and Grade: Fasteners are graded based on their tensile strength (the amount of stress they can withstand). Always select a grade that meets or exceeds the engineering requirements of your application.
Corrosion Resistance: Consider the operating environment. Will the fastener be exposed to moisture, salt, or chemicals? Choose a material or a protective coating (e.g., hot-dip galvanizing, zinc plating) that can withstand the conditions.
Thread Type: Ensure the thread type (e.g., UNC for coarse, UNF for fine) matches the application. Coarse threads are more common and durable, while fine threads provide better tensioning.

Forged for Perfection.
Trusted for Precision.
Delivered with Confidence.
Products
Materials
Contact
- sales@shribhairavforge.com
- +91 9969566209
- +91 22 6636 2333
- Plot 59, Dr M.G Marg, Mumbai - 400004, Maharashtra, India
- Shribhairav Metal Corporation